What is the speck filter?
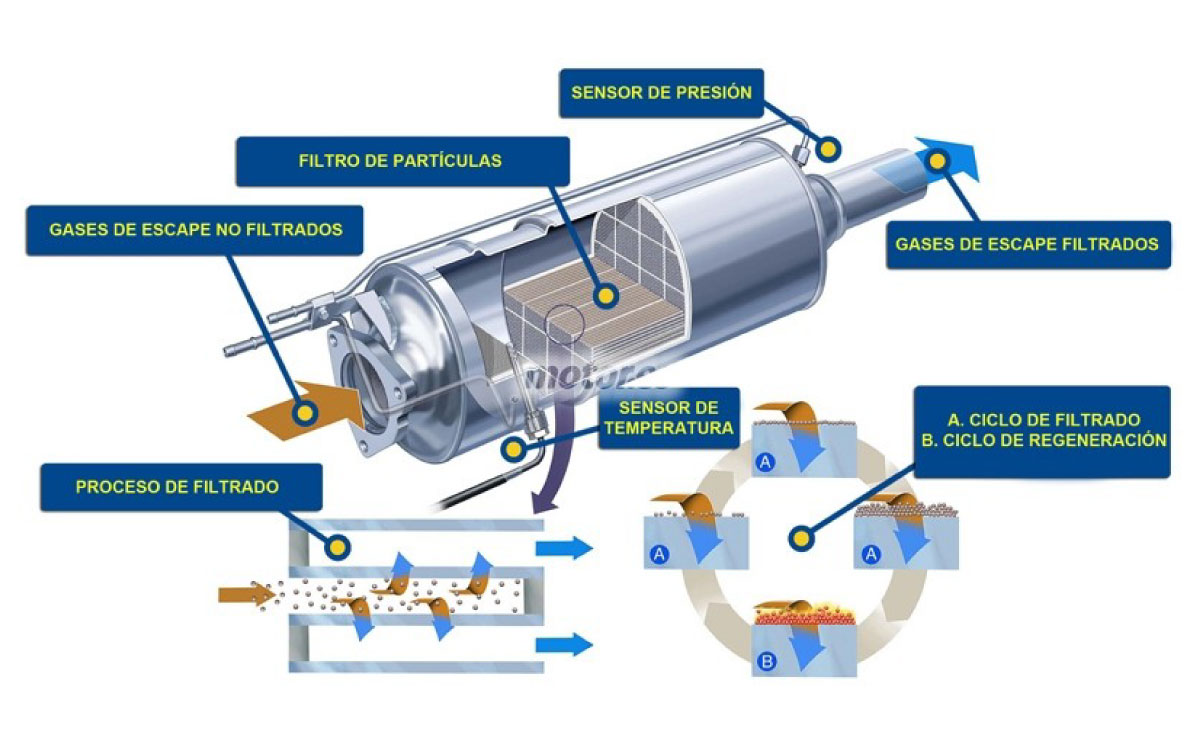
The speck filter is responsible for reducing the soot particles generated during some phases of combustion, reducing the level of polluting specks that are expelled through the exhaust.
WHICH VEHICLES HAVE A SPECK FILTER?
Most diesel engines after 2005 have a built-in speck filter, also known as FAP or DPF, for its acronym in French or English. Explained in a simpler way, what happens is that these solid particles are retained in the porous walls of the filter and are eliminated from time to time in what is called the “regeneration phase”. In this phase, the temperature of the filter is raised to incinerate the soot and clean the system.
WHEN DO THE PROBLEMS OCCUR?
When we start the car, the engine control unit begins to evaluate the values of the different sensors located in the filter. Once the requirements indicated by the manufacturer have been met, the process of regenerating the particulate filter begins.
Since each driver gives a personal and specific use to his car that may not be the most suitable for the perfect functioning of FAP. The most common reason is when the car is used only for urban rides, where it is not possible to reach the minimum temperature necessary for regeneration. As the temperature does not rise enough, the soot is not incinerated which causes the filter to continue accumulating particles without cleaning until it is saturated.
Short journeys, in which the cleaning cycle can be interrupted, are also problematic. To complete, it usually takes between 10 and 25 minutes (the time depends on several factors) driving on the highway at average speed.
In addition to all of the above, the use of an inadequate oil in the engine, shortens the life of the particulate filter by at least 30%.

WHAT HAPPENS WHEN THE FILTER DOES NOT PERFORM REGENERATION?
The filter becomes saturated and usually ignites a light in dashboard to indicate that the system needs a forced regeneration, which entails an inevitable visit to your trusted workshop. The car can still be used, although in some cases the performance is reduced because the electronic system of the engine enters an emergency or breakdown mode to avoid damaging the filter. Another consequence of excessive accumulation of soot in the filter is that regeneration cycles are carried out more frequently and every less kilometer, increasing fuel consumption.
